If you’ve ever wondered how your phone knows where a photo was taken, or how social media tags your location automatically, you’re already familiar with geotagging—even if you didn’t know the term. Let’s dive into the meaning of geotagging, look at real-world examples, and understand how this fascinating tech feature works.
Geotagging Meaning
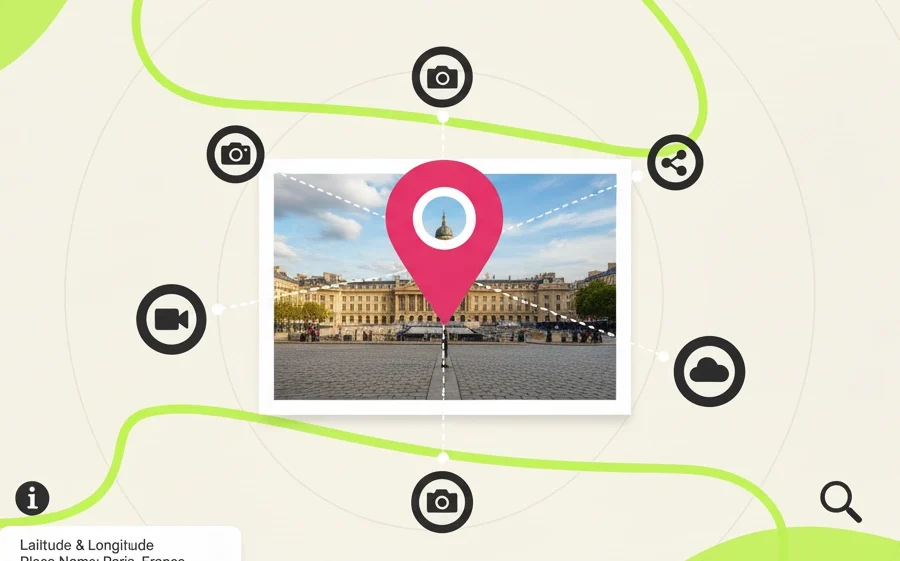
Geotagging (also written as geo-tagging or geolocation tagging) is the process of adding location data to digital content. This usually means embedding latitude and longitude coordinates into files like photos, videos, tweets, and even emails.
In simpler terms, geotagging tells digital content where in the world it was created or posted.
This location metadata is often collected automatically by GPS-enabled devices like smartphones and cameras. So next time your phone says a photo was taken in “Paris, France,” that’s geotagging in action.
What Is a Geotag?
A geotag is the actual piece of information that represents location in a digital file. It can include:
- Latitude and longitude coordinates
- Altitude
- Place names (like a city or landmark)
- Time zone
These tags are embedded in the metadata of digital content, enabling apps and services to organize, filter, and display that content by location.
How Does Geotagging Work?
The process behind geotagging might sound complex, but it’s actually quite straightforward when you break it down. Your device—like a smartphone or digital camera—uses built-in features to figure out where you are. This usually involves GPS signals, nearby Wi-Fi networks, or even nearby cell towers to pinpoint your position.
Here’s how it works in everyday terms:
- Capture: When you snap a photo or record a video, your device figures out your current location.
- Tagging: It then quietly saves that location information—like city, country, or even precise coordinates—inside the file. This is done automatically, without you needing to do anything.
- Sharing: When you later upload that photo or post it on social media, the app may read that location tag and show where the photo was taken, or use it to help others discover content from that area.
All of this happens in the background, almost instantly. Most people never even notice it, but it’s what allows your phone to create albums based on trips or show your photo on a map.
How to View or Remove Geotags
On smartphones:
- iPhone: Open the Photos app and tap on a picture. Swipe up or tap the “Info” (ℹ️) button to see the location where the photo was taken, displayed on a map. To turn off geotagging, go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Location Services > Camera and set it to “Never.”
- Android: Open your gallery or Google Photos, tap on a photo, and look for the location info, often found under “Details” or by swiping up. To stop tagging future photos, open the Camera app, go to its settings, and turn off “Save location.”
If you don’t want to rely solely on your phone’s settings, there are also free tools online that allow you to geolocate images easily. One great option is GeoMakers, a free and user-friendly online tool that helps you add or modify GPS coordinates on your photos—perfect for optimizing images for local SEO or organizing your travel content by place.
Additionally, if you’re curious about the geotags a photo already contains, you can use websites like Jimpl to view and analyze the metadata inside an image file. This can help you better understand what location info is stored in your photos before you share them.
Why Is Geotagging Important?
Geotagging serves many purposes, including:
- Organization: Easily find photos from a specific trip or event. With geotags, digital photo libraries can automatically sort images by city or venue, making it faster to relive memories or create travel logs.
- Discovery: Social media users can explore content from specific places. When users tag content with a location, others can search or browse feeds to discover real-time visuals and reviews from that place.
- Marketing: Businesses can target content to users in specific locations. By integrating geotagged media into websites or ad campaigns, brands improve local engagement and visibility in search results, especially in “near me” queries.
- Analysis: Governments and researchers use geotagged data for planning and trend analysis. This includes urban development, traffic management, public safety response patterns, and even environmental monitoring through citizen-shared content.
- Local SEO: Geotagging images and website content helps local businesses rank higher in geographically relevant search results. It signals search engines about the service area or storefront location, reinforcing relevance for local queries.
- Google Business Profile Optimization: Uploading geotagged photos to your GMB listing supports stronger verification signals for your physical presence. Google may reward this with better placement in the map pack, increased trust signals, and higher visibility to users nearby.
Risks and Considerations
Despite its benefits, geotagging comes with potential downsides:
- Privacy concerns: Sharing geotagged content publicly can unintentionally reveal your home, workplace, or daily routines.
- Security risks: Posting real-time location can expose you to theft or stalking.
That’s why many apps allow you to disable location tagging or strip metadata before sharing.
Final Thoughts
Geotagging might sound technical, but it’s become a part of daily life. Whether you’re posting a vacation selfie or analyzing delivery routes, geotags make digital content smarter and more useful.
Now that you know what geotagging means, how it works, and where it’s used, you’ll start noticing it everywhere—and hopefully, you’ll be able to make the most of it while keeping your privacy in check.